
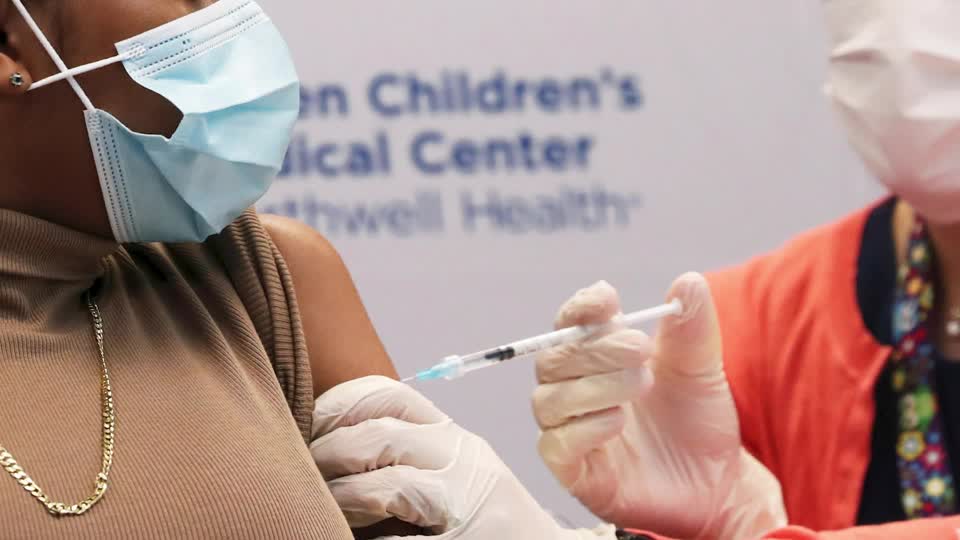
COVID-19 vaccines are not associated with a higher risk of adverse effects during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. Ĭommon side effects of COVID-19 vaccines include soreness, redness, rash, inflammation at the injection site, fatigue, headache, myalgia (muscle pain), and arthralgia (joint pain), which resolve without medical treatment within a few days. Many countries implemented phased distribution plans that prioritized those at highest risk of complications, such as the elderly, and those at high risk of exposure and transmission, such as healthcare workers. According to a June 2022 study, COVID-19 vaccines prevented an additional 14.4 to 19.8 million deaths in 185 countries and territories from 8 December 2020 to 8 December 2021. The COVID‑19 vaccines are widely credited for their role in reducing the spread of COVID-19 and reducing the severity and death caused by COVID‑19, though some people have still managed to get the virus even after being vaccinated. However, immunity from the vaccines has been found to wane over time, requiring people to get booster doses of the vaccine to maintain immunity against COVID-19. Initially, most COVID-19 vaccines were two-dose vaccines, with the sole exception being the single-dose Janssen COVID-19 vaccine. In 2020, the first COVID-19 vaccines were developed and made available to the public through emergency use authorization. On 10 January 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 genetic sequence data was shared through GISAID, and by 19 March, the global pharmaceutical industry announced a major commitment to address COVID‑19. The initial focus of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was on preventing symptomatic, often severe illness. This knowledge accelerated the development of various vaccine platforms during early 2020. Prior to the COVID‑19 pandemic, an established body of knowledge existed about the structure and function of coronaviruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).

Monitoring COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths by Vaccination Status.How and Why CDC Measures Vaccine Effectiveness.
#SIDE EFFECT OF COVID BOOSTER PLUS#
COVID-19 Vaccines are Effective plus icon.Investigating Long-Term Effects of Myocarditis.Possibility of COVID-19 Illness after Vaccination.Stay Up to Date with Vaccines plus icon.Why Children & Teens Should Get Vaccinated.Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System can be used by you or your healthcare provider to report a side effect, adverse event, or reaction from the COVID-19 vaccine.

Adverse Events after COVID-19 Vaccination Are RareĪdverse events, including severe allergic reactions, after COVID-19 vaccination are rare but can happen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
